Elevating Hearing Health
on the Political Agenda
Hearing loss is a major public health challenge affecting millions across Europe, yet it remains widely overlooked. To address this growing issue, we call for a comprehensive European Hearing Health Strategy that places hearing health higher on the political agenda and ensures equitable access to care for all.

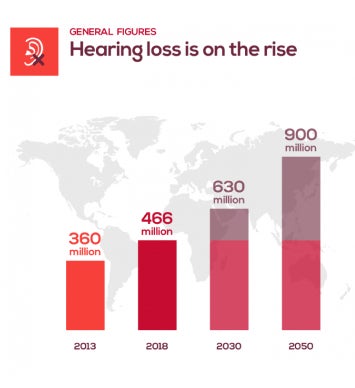
Silent Challenges of Hearing Loss
live with hearing loss
access to hearing care
Our HEAR Strategy

Hearing Loss
Awareness

Early Detection
& Prevention

Access
& Care

Research
& Data
Join our Efforts: Endorse the Policy Manifesto
We call on the European Commission to take action. By signing the Manifesto, you are supporting our efforts in advocating for a European Hearing Health Strategy!

Stay Up to Date
Stay informed about the latest updates, research findings, and initiatives by following us on LinkedIn. Get involved and be part of the conversation.
Follow on LinkedIn
About Us
We are the Hearing Health Forum EU, committed to promoting inclusive, lifelong hearing care, supporting early detection, and advocating for effective policies and research that enhance quality of life and strengthen Europe’s health systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Find answers to the most common questions about hearing loss, access to care, and our advocacy work across Europe.